Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) measurements in the city of Aachen
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is produced in particular during combustion processes: The main sources in the city are road traffic and, in winter, combustion plants for coal, oil, gas, wood, etc. As an irritant gas, NO2 mainly affects the lower respiratory tract. High levels can occur for short periods on busy roads, which can lead to acute irritation, coughing and long-term deterioration of lung function. NO2 is also a precursor for the formation of particulate matter and ground-level ozone. Ozone (O3) is also a harmful irritant gas and damages the lungs. Particulate matter is much more harmful to health than nitrogen dioxide (per unit mass). It leads to a large number of acute and chronic health effects, from effects on the respiratory tract, cardiovascular system and metabolism to increased mortality[1].
Clean air is crucial for people's health. To this end, the EU sets air quality standards to protect health.
[1] Source: Federal Environment Agency, FAQ on the subject of nitrogen dioxide
Measurements by the LANUV
Monitoring air quality in NRW is basically the responsibility of the state. For this purpose, the State Agency for Nature, Environment and Climate NRW (LANUK) maintains measuring containers in the city of Aachen on Wilhelmstraße (at house number 22/24, traffic station) and in Burtscheid (meadow area Hein-Görgen-Straße, urban background pollution). LANUK also carries out measurements of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) using the passive sampler method in the Adalbertsteinweg area (at house number 5) and in Haaren (at Alt-Haarener Straße 18).
Descriptions of the exact measurement locations and the air quality parameters recorded
Measurements of the city of Aachen
As part of clean air planning, the city has been working to improve air quality in Aachen since the 1990s. To this end, the current Climate and Environment Department carries out its own nitrogen dioxide measurements using passive samplers at various locations in the city.
In the early years of clean air planning, the city measured NO2 levels at various locations over several weeks and months. These measurements served as so-called orientation measurements to identify local peculiarities and pollution hotspots. Measurements were taken in the valley basin, particularly on roads with heavy traffic, in the surrounding urban area (higher and better ventilated than the valley basin) and in the Burtscheid and Monheimsallee spa areas (special measurements in accordance with the Health Resorts Act).
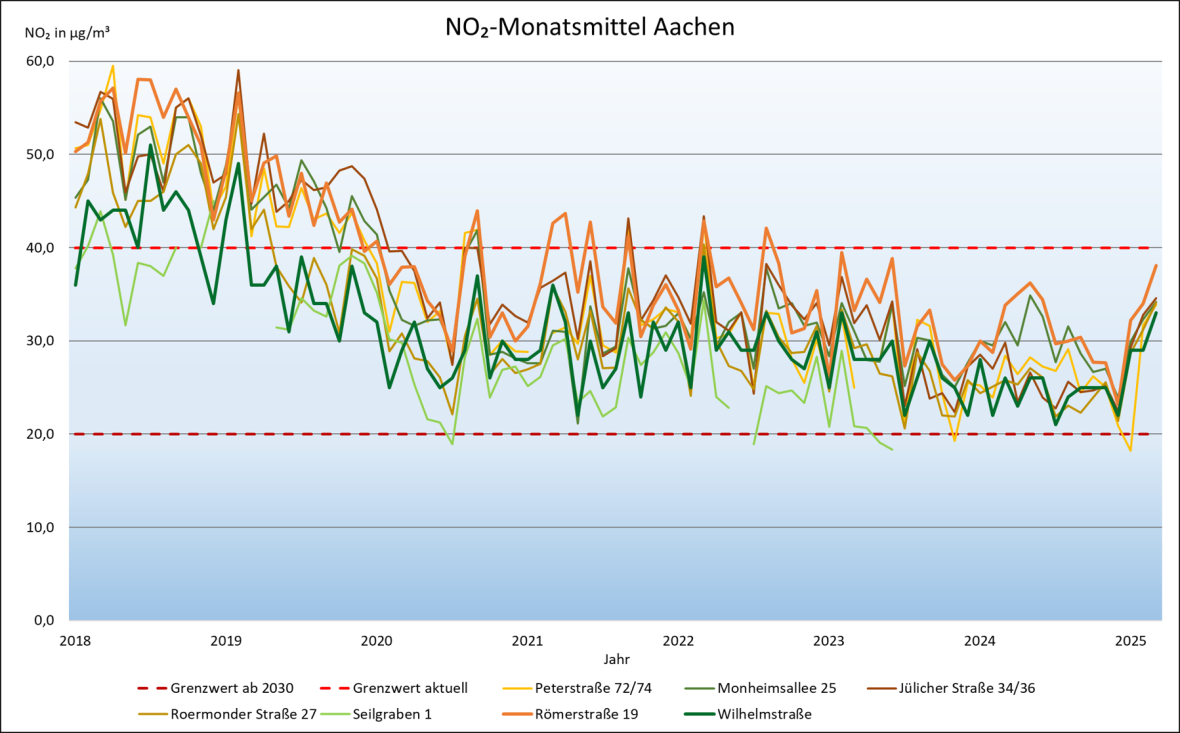
Air quality has improved significantly in recent years, partly due to the implementation of immediate measures from the LRP 2019 (e.g. retrofitting and upgrading the ASEAG bus fleet with low-emission drive technology, reducing parking search traffic by harmonizing parking fees, closing the Büchel multi-storey parking lot, 30 km/h in the city centre, etc.). The previous NO2 limit value of 40 µg/m³ has been clearly undercut since 2020.
Current measuring points of the city of Aachen (since 01/2024):
The city currently records NO2 pollution at the traffic-related pollution hotspots
- Römerstrasse 19
- Peterstrasse 72/74
- Monheimsallee 25
- Jülicher Strasse 34/36
- Roermonder Straße 27
- Von-Coels-Str. 4 / Berliner Ring
- Adalbertsteinweg 274
Graphic on the development of NO2 values at selected pollution hotspots